Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) focuses on optimizing digital assets like websites through AI-driven content creation and user experience refinement. In contrast, Search Generative Experiences (SGE) personalize search results and interactions using AI, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement with dynamically generated content tailored to individual preferences and contexts.
Table Of Content
In this article we will talk about ‘Difference Between GEO and SGE’

Introduction to Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) represents a cutting-edge approach to enhancing digital experiences through advanced algorithmic techniques. Unlike traditional SEO (Search Engine Optimization), which focuses primarily on content relevance and technical optimization, GEO leverages generative AI technologies to dynamically create and optimize content, user interfaces, and interactive experiences in real time.
At its core, GEO harnesses the power of machine learning models to adapt and refine digital assets continuously. By analyzing user behavior, preferences, and contextual data, GEO algorithms iteratively generate and optimize content in real time to deliver personalized and engaging experiences across various digital platforms.
This introduction sets the stage for exploring how GEO revolutionizes digital marketing strategies and enhances user engagement through adaptive and responsive content creation.
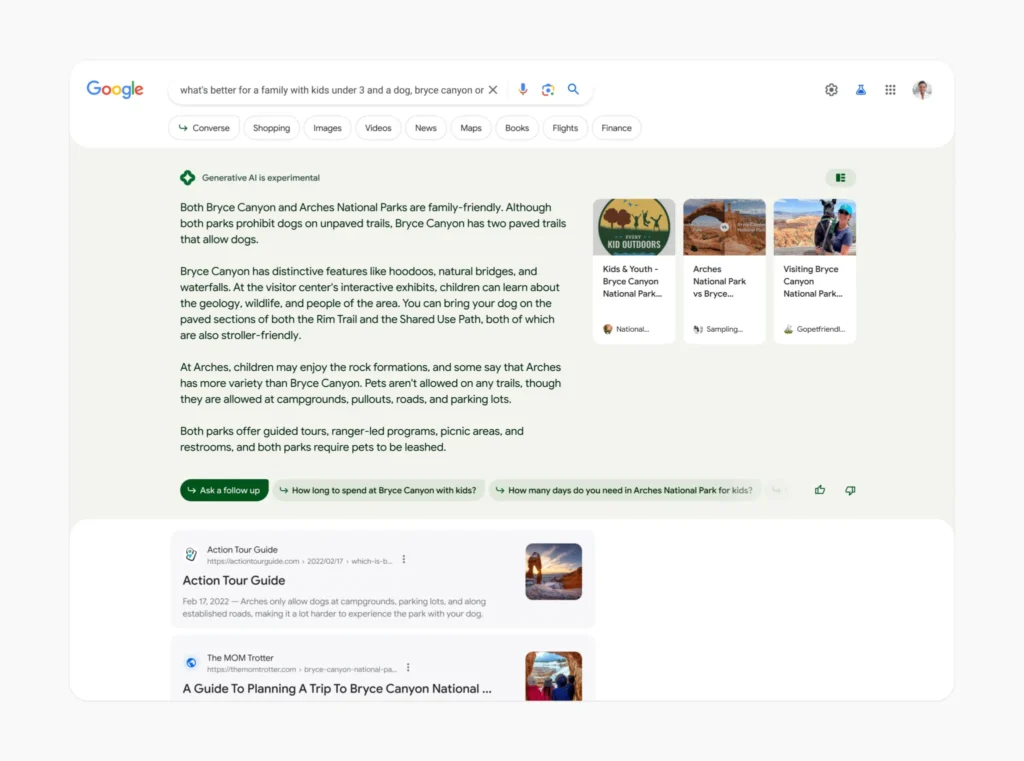
Introduction to Search Generative Experiences (SGE)
Search Generative Experiences (SGE) represent a paradigm shift in how users interact with digital content and services. Unlike traditional search engines that retrieve static information based on keyword queries, SGE integrates generative AI technologies to dynamically generate and customize content in response to user inputs and context.
At its essence, SGE leverages advanced machine learning algorithms to understand user intent, preferences, and contextual information. By generating tailored responses, recommendations, and interactive interfaces in real content in a real-time context, SGE aims to enhance user engagement and satisfaction significantly.
This introduction highlights the transformative potential of SGE in delivering personalized and adaptive digital experiences across various domains, from e-commerce and customer service to content consumption and interactive applications. As we delve deeper into SGE, we’ll explore its core principles, technological foundations, and practical applications that redefine user interactions in the digital age.
Understanding Search Generative Experiences (SGE) and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Understanding Search Generative Experiences (SGE)
Search Generative Experiences (SGE) leverage generative AI technologies to dynamically generate and customize content based on user queries and contextual data. Unlike traditional search engines that retrieve pre-existing information, SGE systems use machine learning models to understand user intent, preferences, and the query context. This allows them to generate personalized responses, recommendations, and interactive interfaces in real time, enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
Key aspects of SGE:
- Dynamic Content Generation: SGE systems produce flyquery material that is customized to each user’s requirements and tastes.
- Personalization: They adapt responses based on user behavior, historical data, and real-time interactions to provide relevant and engaging experiences.
- Contextual Understanding: SGE algorithms analyze the context of queries, incorporating factors such as location, time, and user history to refine generated content.
Understanding Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), on the other hand, applies generative AI techniques to optimize digital assets such as websites, applications, and marketing campaigns. Rather than focusing solely on static content and SEO principles, GEO dynamically creates and optimizes content to improve user experience, engagement metrics, and conversion rates.
Key Aspects of GEO:
- Dynamic Content Creation: GEO algorithms generate and optimize content continuously, adapting to user interactions and preferences.
- Algorithmic Optimization: It uses machine learning models to analyze user data and behavior, refining content presentation and delivery.
- Enhanced User Experience: GEO aims to deliver personalized and responsive digital experiences that align with user expectations and business goals.
The major difference between GEO and SGE
The key difference between Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and Search Generative Experiences (SGE) lies in their primary objectives and areas of application:
- Objective:
- GEO (Generative Engine Optimization): GEO focuses on optimizing digital assets, such as websites, applications, and digital content, through the use of generative AI techniques. The primary goal of GEO is to enhance the user experience, engagement metrics (like time on site and interaction rates), and conversion rates by dynamically generating and optimizing content based on user behavior and real-time data analytics.
- SGE (Search Generative Experiences): SGE is centered around improving the search and interaction experiences for users. It uses generative AI technologies to dynamically generate and customize content in response to user queries and contextual information. The main objective of SGE is to deliver personalized search results, recommendations, and interactive interfaces that adapt to individual user preferences and behaviors.
- GEO (Generative Engine Optimization): GEO focuses on optimizing digital assets, such as websites, applications, and digital content, through the use of generative AI techniques. The primary goal of GEO is to enhance the user experience, engagement metrics (like time on site and interaction rates), and conversion rates by dynamically generating and optimizing content based on user behavior and real-time data analytics.
- Application:
- GEO: Implemented across various digital platforms and marketing channels, GEO focuses on optimizing content delivery and user interactions to achieve specific business objectives, such as increased conversions or brand engagement. It involves the continuous refinement of content creation processes based on algorithmic analysis of user data and behavior.
- SGE: Typically integrated into search engines, digital assistants, and interactive applications, SGE enhances the search experience by generating tailored responses and recommendations. It aims to improve user satisfaction and interaction quality by understanding user intent, context, and preferences, thereby delivering more relevant and personalized search results.
- GEO: Implemented across various digital platforms and marketing channels, GEO focuses on optimizing content delivery and user interactions to achieve specific business objectives, such as increased conversions or brand engagement. It involves the continuous refinement of content creation processes based on algorithmic analysis of user data and behavior.
- Impact:
- GEO: The impact of GEO is seen in improved performance metrics for digital assets, including higher engagement rates, reduced bounce rates, and increased conversion rates. It focuses on optimizing the user journey and content effectiveness through data-driven insights and continuous optimization.
- SGE: SGE enhances user satisfaction and engagement by providing more relevant and personalized search results and interactive experiences. It aims to increase user retention and interaction quality through adaptive content generation and responsive interfaces that cater to individual user needs.
- GEO: The impact of GEO is seen in improved performance metrics for digital assets, including higher engagement rates, reduced bounce rates, and increased conversion rates. It focuses on optimizing the user journey and content effectiveness through data-driven insights and continuous optimization.
In essence, while both GEO and SGE utilize generative AI technologies, GEO focuses on optimizing digital assets and content for improved performance and user experience, while SGE enhances search and interaction experiences by dynamically generating personalized content and recommendations based on user queries and context.
Key Objectives and Goals of GEO and SGE
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Objectives and Goals:
- Enhanced User Experience: GEO aims to optimize digital assets such as websites, applications, and content to provide users with a more engaging and personalized experience. This includes improving usability, accessibility, and content relevance tailored to user preferences.
- Improved Engagement Metrics: GEO seeks to increase user engagement metrics such as time spent on site, interaction rates, and pages per session. By dynamically generating and optimizing content, GEO aims to capture and maintain user interest more effectively.
- Higher Conversion Rates: One of the primary goals of GEO is to drive conversions by presenting optimized content and calls-to-action that resonate with users’ needs and behaviors. This could involve personalized recommendations, targeted offers, and optimized landing pages.
- Continuous Optimization: GEO involves ongoing optimization based on real-time data analysis and user feedback. The goal is to adapt content delivery strategies dynamically to maximize performance and achieve business objectives.
- Brand Perception and Loyalty: By delivering consistent and high-quality user experiences, GEO aims to enhance brand perception, build trust, and foster customer loyalty over time.
Search Generative Experiences (SGE)
Objectives and Goals:
- Personalized Search Results: SGE focuses on delivering personalized search experiences by understanding user intent, preferences, and contextual information. The goal is to provide relevant and tailored search results that match individual user needs more effectively than traditional search engines.
- Enhanced User Satisfaction: By generating dynamic and contextually relevant content, SGE aims to improve user satisfaction with search results and overall interaction quality. This includes reducing search fatigue and frustration by presenting more accurate and useful information.
- Increased Engagement and Interaction: SGE seeks to increase user engagement with search interfaces and interactive applications by offering personalized recommendations, suggestions, and interactive elements that encourage further exploration and interaction.
- Adaptive Content Generation: The goal of SGE is to dynamically generate content and responses based on evolving user queries and contextual signals. This adaptive approach helps to stay relevant and responsive to changing user needs and preferences.
- Improved User Retention: By delivering satisfying and personalized search experiences, SGE aims to enhance user retention and loyalty. This is achieved through consistently meeting user expectations and providing value-added interactions.
In summary, while GEO focuses on optimizing digital assets for improved user experience, engagement, and conversion rates through dynamic content optimization, SGE is geared towards enhancing search and interaction experiences by delivering personalized and contextually relevant content and responses. Both approaches leverage generative AI technologies but serve distinct goals within the realm of digital strategy and user engagement.
Implementation Strategies for SGE and GEO
implementing Search Generative Experiences (SGE) and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) involves strategic planning and leveraging specific techniques tailored to each approach. Here are some implementation strategies for SGE and GEO:

Implementation Strategies for Search Generative Experiences (SGE):
- Data Integration and Analysis:
- Strategy: Integrate diverse data sources, including user behavior, preferences, and contextual data (like location and time), to create a comprehensive understanding of user intent.
- Implementation: Utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze and interpret this data, enabling the generation of personalized search results and recommendations.
- Strategy: Integrate diverse data sources, including user behavior, preferences, and contextual data (like location and time), to create a comprehensive understanding of user intent.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Understanding:
- Strategy: Implement advanced NLP techniques to comprehend and interpret user queries in natural language.
- Implementation: Develop models that can extract key intents and entities from user input to refine search results and provide more accurate responses.
- Dynamic Content Generation:
- Strategy: Enable real-time generation of content and responses based on user queries and contextual data.
- Implementation: Implement generative AI models that can dynamically create personalized content, such as product recommendations, tailored articles, or interactive interfaces.
- Personalization Algorithms:
- Strategy: Build algorithms that adaptively personalize search experiences based on user interactions and historical data.
- Implementation: Utilize machine learning models to predict user preferences and behavior, delivering customized content recommendations and search results in real time.
- User Interface Design:
- Strategy: Design intuitive and interactive user interfaces that enhance the search and discovery process.
- Implementation: Incorporate features such as autocomplete suggestions, voice search capabilities, and visual search options to improve user engagement and ease of use.
- Feedback and Iterative Improvement:
- Strategy: Implement mechanisms to gather user feedback and behavioral data continuously.
- Implementation: Use feedback loops to refine algorithms, improve the relevance of search results, and address user preferences dynamically over time.
Implementation Strategies for Generative Engine Optimization (GEO):
- Content Optimization and Generation:
- Strategy: Develop algorithms to optimize and generate content dynamically across digital platforms.
- Implementation: Use generative AI to create personalized landing pages, product descriptions, and marketing content that resonates with specific audience segments.
- SEO and Technical Optimization:
- Strategy: Combine traditional SEO techniques with AI-driven insights to enhance the technical aspects of websites and applications.
- Implementation: Utilize AI for keyword analysis, semantic search optimization, and structured data markup to improve visibility and ranking in search engine results.
- User Experience Enhancement:
- Strategy: Focus on improving user interface design and navigation to optimize the user experience.
- Implementation: Implement AI-driven tools for A/B testing, heatmaps, and user journey analysis to identify and address pain points, thereby increasing engagement and conversion rates.
- Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO):
- Strategy: Employ AI algorithms to analyze user behavior and optimize conversion funnels.
- Implementation: Use predictive analytics and personalized content recommendations to increase conversion rates through targeted offers, persuasive messaging, and optimized call-to-actions.
- Performance Monitoring and Analytics:
- Strategy: Establish robust analytics frameworks to monitor performance metrics and user interactions.
- Implementation: Utilize AI-powered analytics tools for real-time data analysis, trend identification, and performance forecasting to guide ongoing optimization efforts.
- Adaptation to Market Trends:
- Strategy: Stay agile and responsive to market trends and consumer preferences.
- Implementation: Use AI-powered trend analysis and predictive modeling to anticipate changes in user behavior and adjust content strategies accordingly to maintain competitiveness.
By strategically implementing these approaches, organizations can effectively harness the power of generative AI to enhance search experiences (SGE) and optimize digital assets (GEO), ultimately driving improved user engagement, satisfaction, and business outcomes.
GEO VS SGE
Here’s a comparative analysis of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and Search Generative Experiences (SGE) presented in a chart format:
| Aspect | Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) | Search Generative Experiences (SGE) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Optimizing digital assets (websites, applications, and content) | Enhancing search and interaction experiences |
| Goal | Improve user experience, engagement metrics, and conversion rates | Deliver personalized search results, enhance user satisfaction |
| Implementation Area | Digital marketing, content management | Search engines, digital assistants, and interactive applications |
| Techniques Used | AI-driven content generation, optimization | AI-driven dynamic content generation, personalization algorithms |
| Key Features | Dynamic content creation, user journey optimization | Personalized search results, contextual understanding |
| Data Usage | User behavior, real-time analytics | User queries, preferences, and contextual data |
| Impact | Higher engagement, improved conversion rates | Enhanced user satisfaction, increased interaction quality |
| Example Applications | E-commerce platforms, digital advertising campaigns | Search engines, customer support chatbots |
| Tools and Technologies | Machine learning, natural language processing (NLP) | NLP models, recommendation systems |
| Feedback and Iteration | Continuous optimization based on user data and insights | Adaptive content generation, real-time feedback loops |
| Outcome | Enhanced brand perception, increased ROI | Improved user retention, personalized user experiences |
This comparative chart highlights the distinct focuses, goals, implementation areas, techniques used, and outcomes of GEO and SGE. It demonstrates how each approach leverages generative AI technologies to achieve specific objectives within digital strategy and user engagement.
Conclusion: Choosing Between GEO and SGE
Both generative engine optimization (GEO) and search generative experiences (SGE) leverage generative AI technologies to enhance digital interactions and optimize user experiences. The decision to prioritize one over the other should align with your organization’s strategic goals and the nature of your digital presence.
- GEO (Generative Engine Optimization):
- Focus: Optimizes digital assets such as websites, applications, and content.
- Benefits: Improves user experience, engagement metrics, and conversion rates through dynamic content generation and optimization.
- Ideal for: organizations aiming to enhance brand perception, drive conversions, and optimize the performance of digital marketing efforts.
- Example Use Cases: E-commerce platforms, content-driven websites, digital advertising campaigns.
- SGE (Search Generative Experiences):
- Focus: Enhances search and interaction experiences through personalized content generation.
- Benefits: It delivers personalized search results, improves user satisfaction, and increases interaction quality by adapting to user queries and preferences.
- Ideal for: Businesses prioritizing user-centric search experiences, customer support automation, and interactive applications.
- Example Use Cases: Search engines, digital assistants, customer service chatbots.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)?
- GEO, or Generative Engine Optimization, involves optimizing content and user experiences within a specific website or digital platform. It utilizes algorithms and generative models to create content that appeals to users and ranks well on search engines.
2. What is SGE (Search Generative Experiences)?
- SGE, or Search Generative Experiences, focuses on creating interactive features directly within search engine results pages (SERPs). It aims to provide valuable information and engagement directly on the search results page, rather than directing users to a specific website.
3. How do GEO and SGE differ in focus?
- GEO primarily concentrates on optimizing content and experiences within a website or platform, while SGE focuses on creating interactive experiences directly within search results.
4. What are the implementation strategies for GEO and SGE?
- GEO implementation involves optimizing website content, metadata, and user interfaces using AI-powered tools and structured data. SGE implementation focuses on creating interactive features such as calculators, quizzes, or chatbots directly within search results.
5. How do users interact with GEO and SGE?
- Users interact with GEO-optimized content by visiting the website and engaging with its content and features. SGE allows users to interact with features directly on the search results page, providing instant answers or experiences without needing to visit a website.
6. What is the purpose of GEO and SGE?
- The primary purpose of GEO is to drive organic traffic to a website by improving search engine visibility and providing valuable content and experiences. SGE aims to enhance the search experience by providing immediate answers or tools directly within search results, reducing the need to visit multiple websites.








