How to Identify the Source of Direct Traffic (GA4)
To identify direct traffic sources in GA4, select Acquisition, then Traffic Acquisition from the menu options. Add “Landing page” as a secondary dimension to view specific pages receiving direct traffic. Analyze landing pages for patterns or unexpected high-traffic pages. Examine referral sources to check for any references. Monitor direct traffic changes over time.
step-by-step guide on how to identify the source of direct traffic in Google Analytics 4 (GA4):
- Open your web browser and go to analytics.google.com. • Sign in with your Google account; • Select the property you want to analyze.
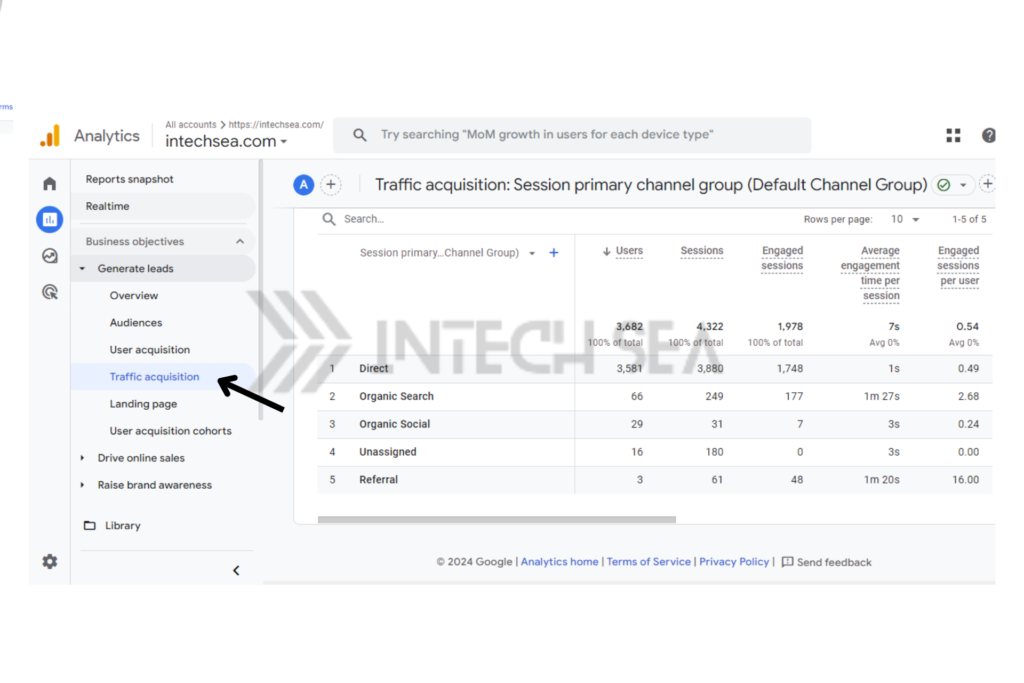
- Navigate to the Traffic Acquisition Report. • In the left-hand menu, click on “Reports.” • Click “Generate leads” Under Generate leads, Click on “Traffic Acquisition.”
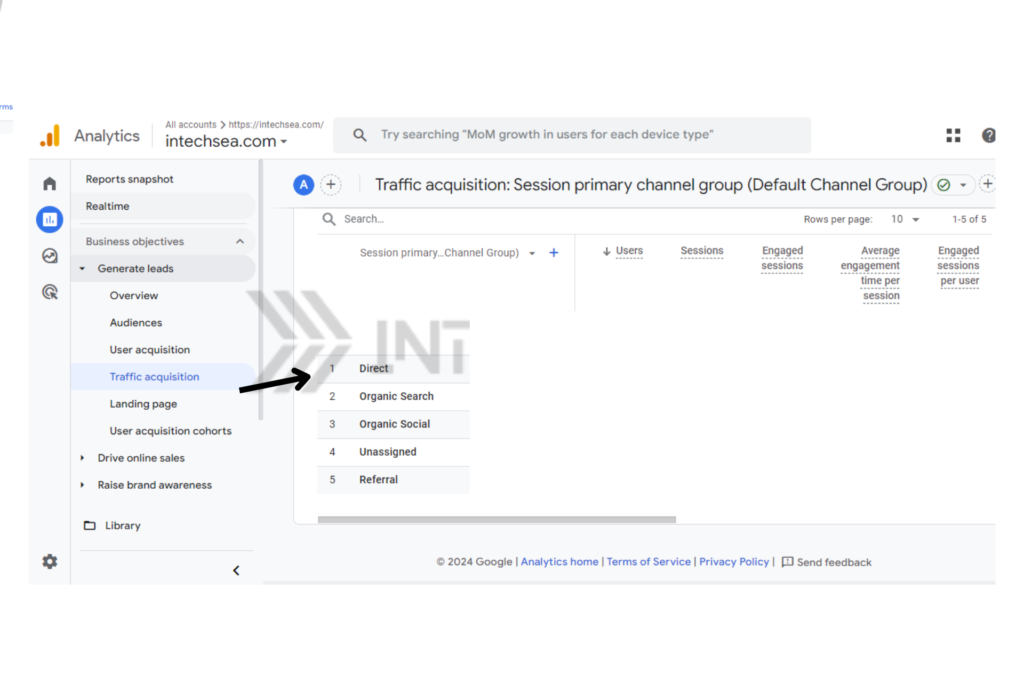
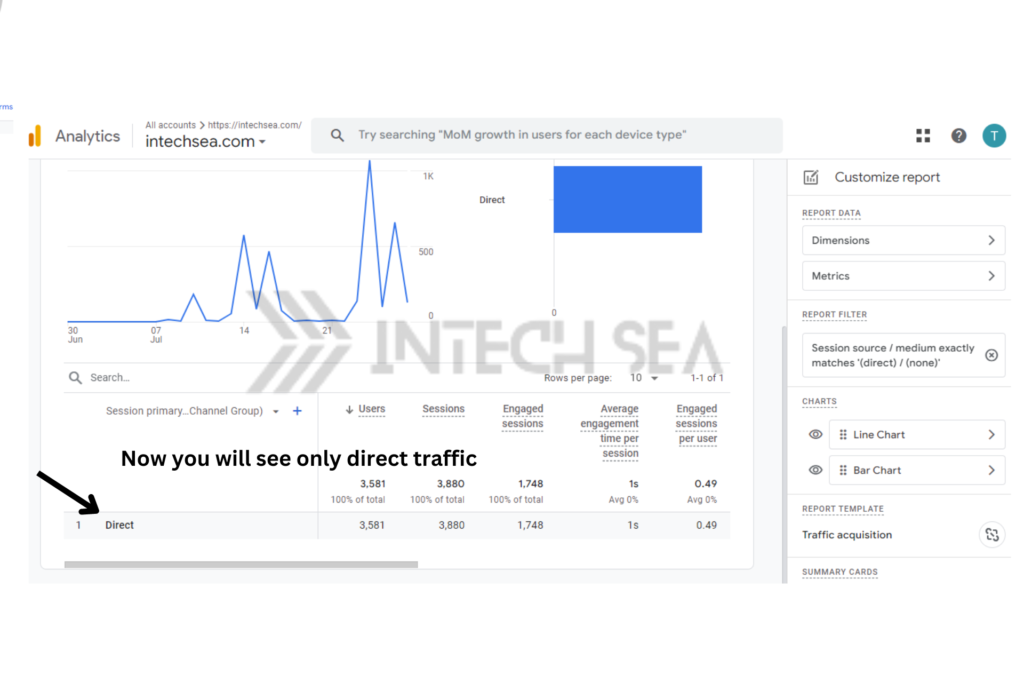
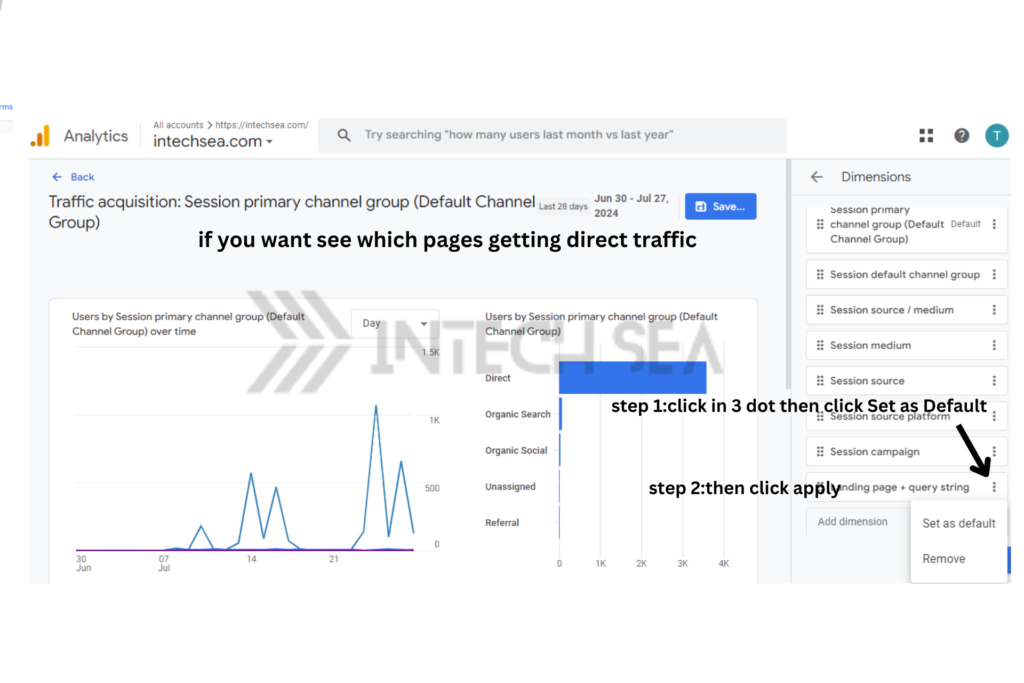
- Locate Direct Traffic Data • In the report, find the row labeled “Direct” under the “Session default channel grouping” dimension • This shows the overall volume of direct traffic to your site.
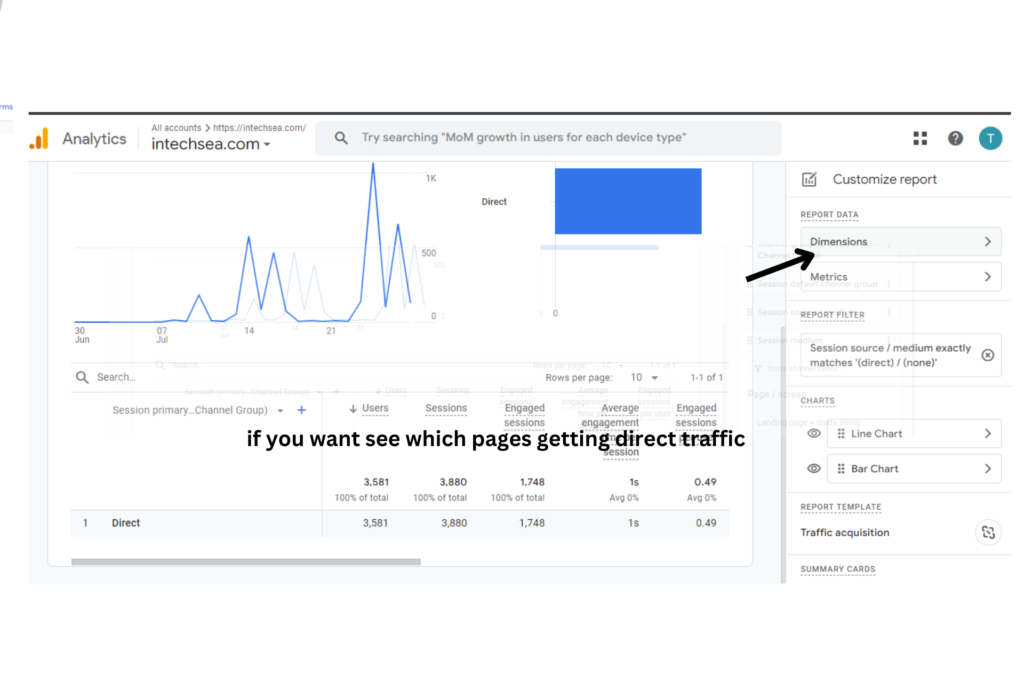
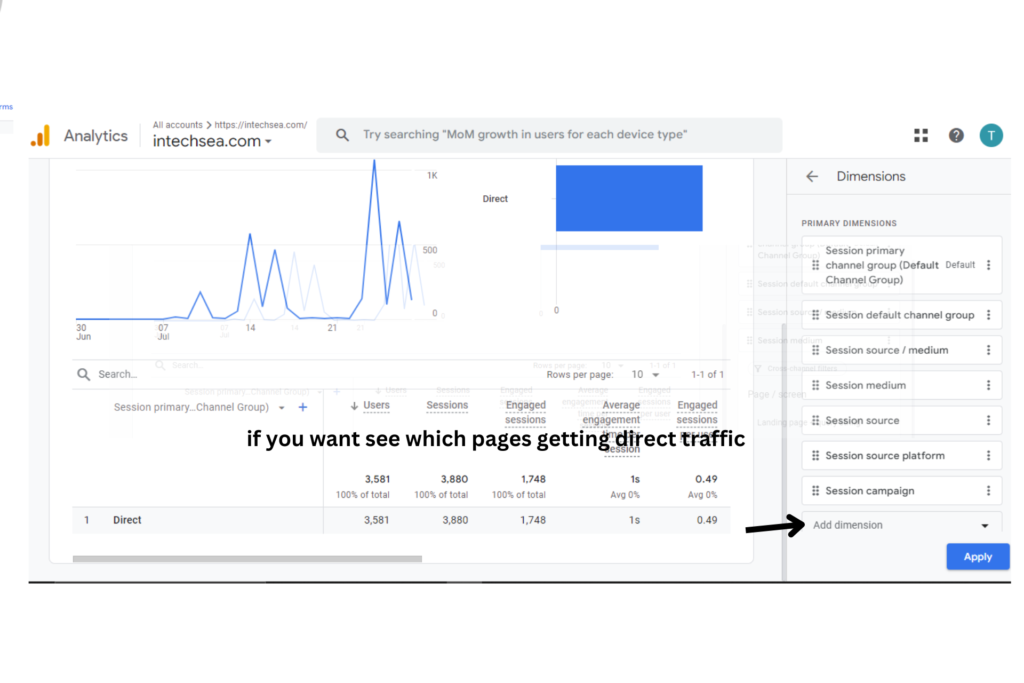
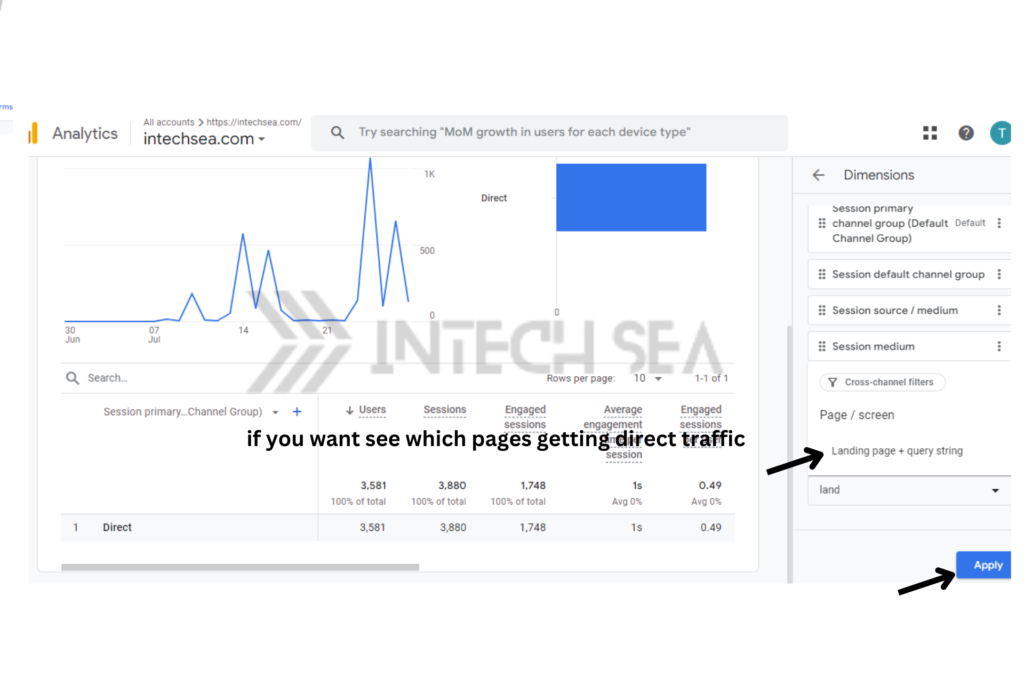
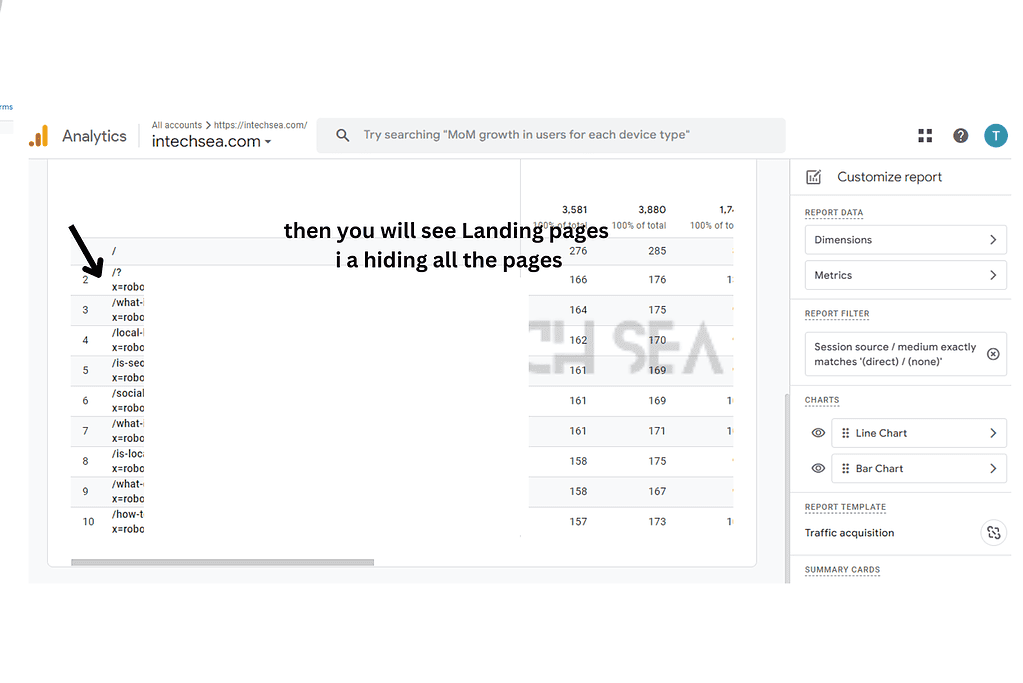
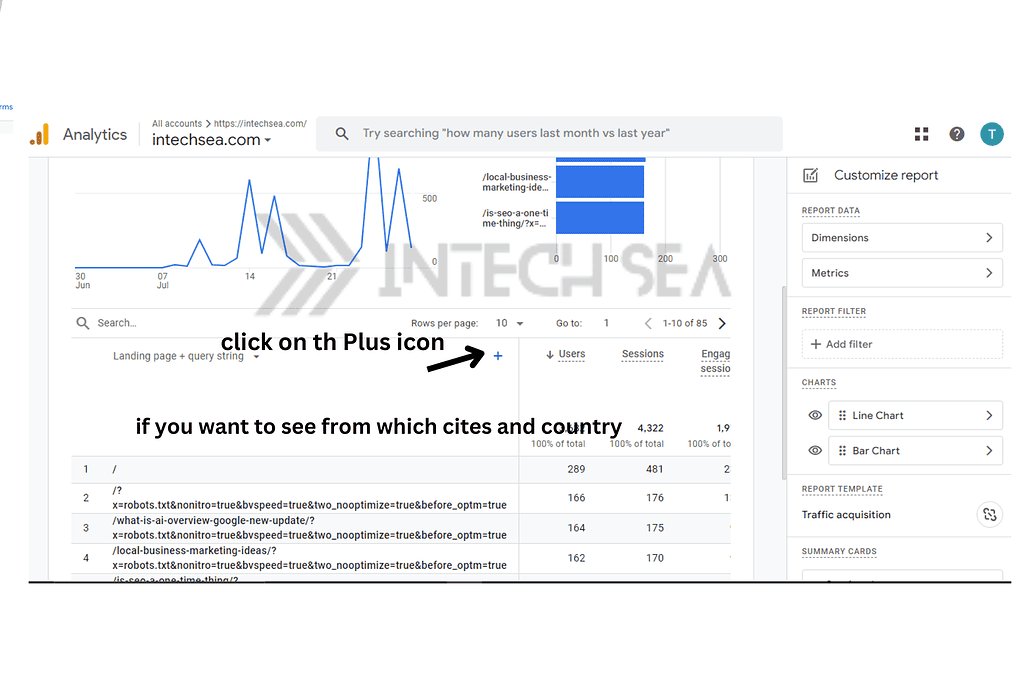
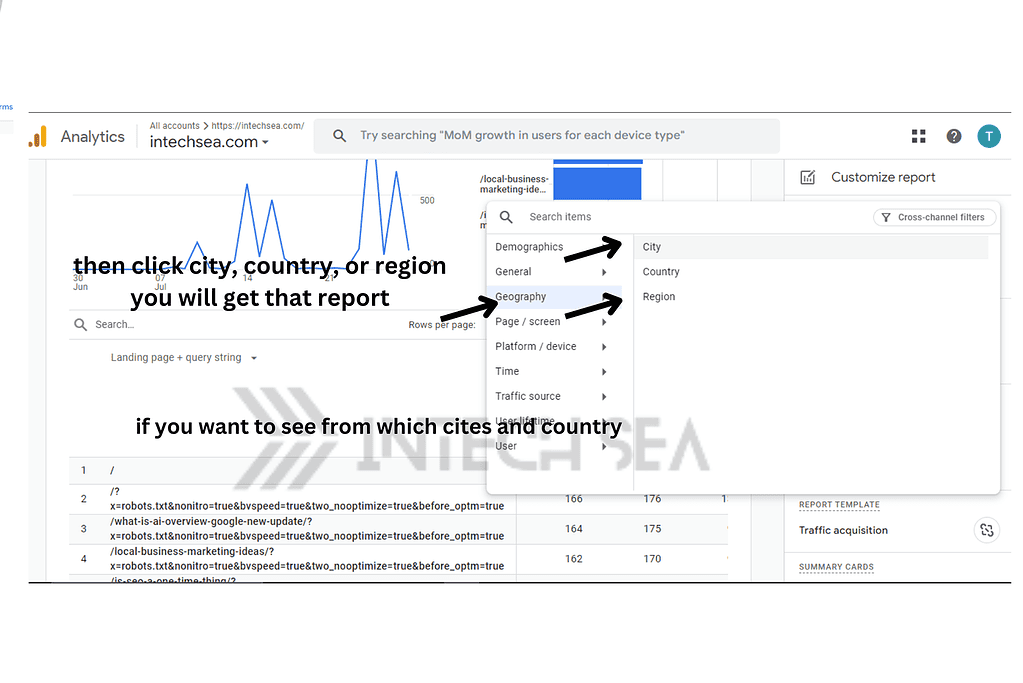
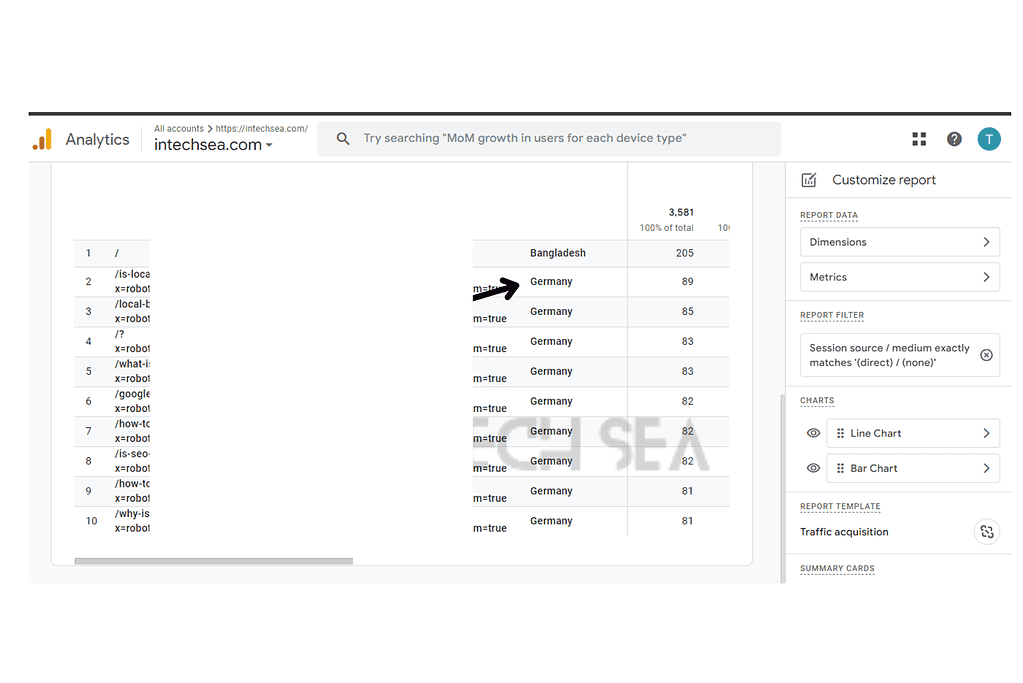
- Analyze Landing Pages for Direct Traffic • In the report, click on “Landing page” as a secondary dimension • This displays the specific pages users are landing on from direct traffic • Look for patterns or unexpected pages receiving high direct traffic
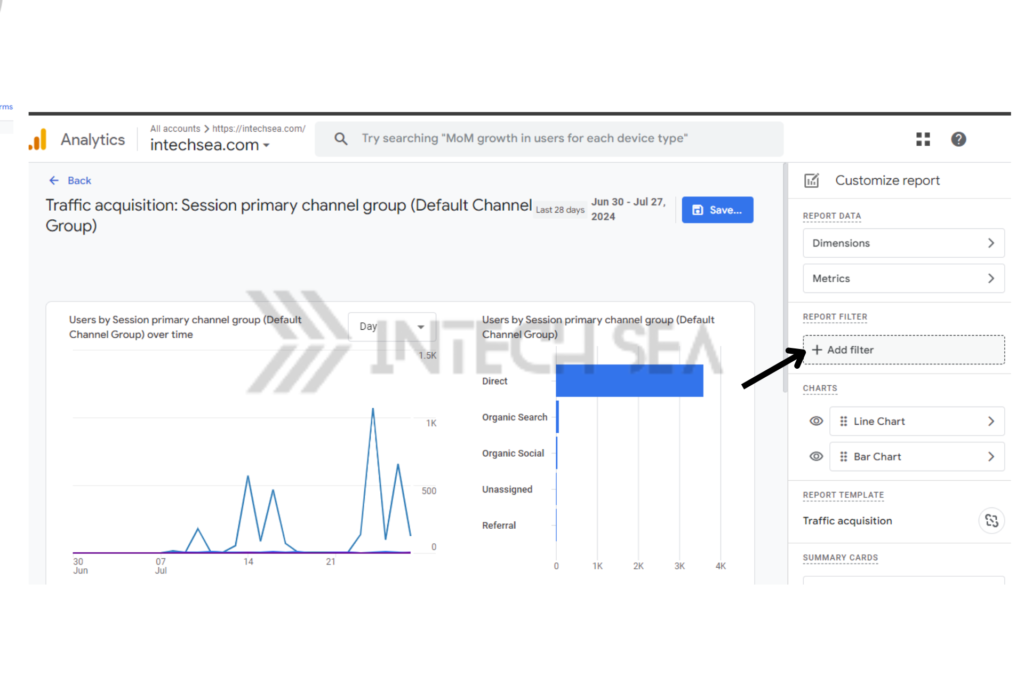
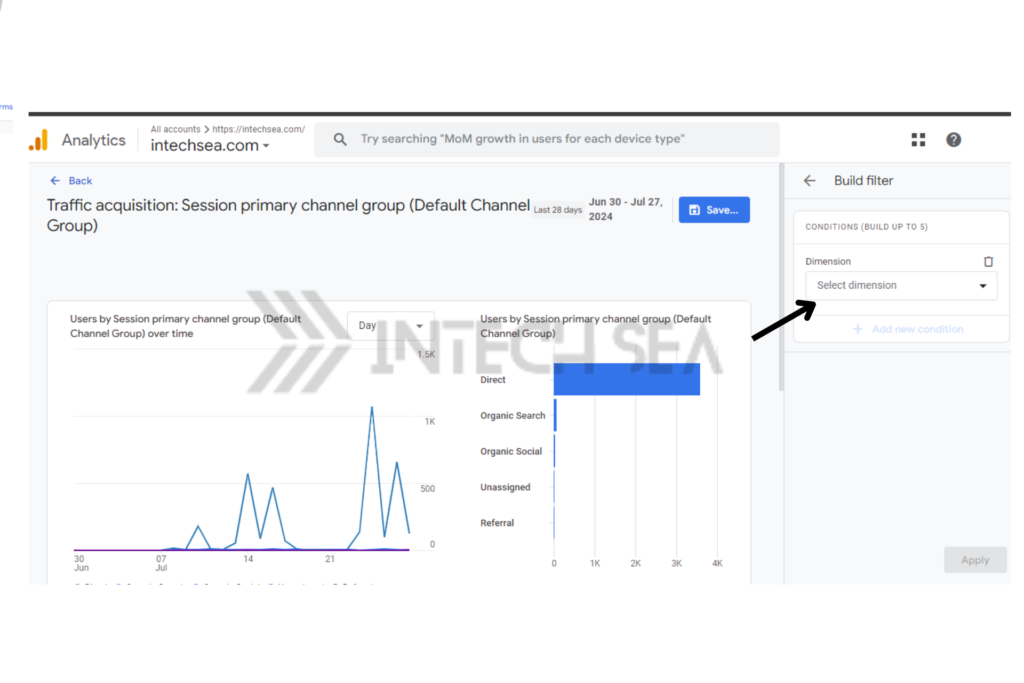
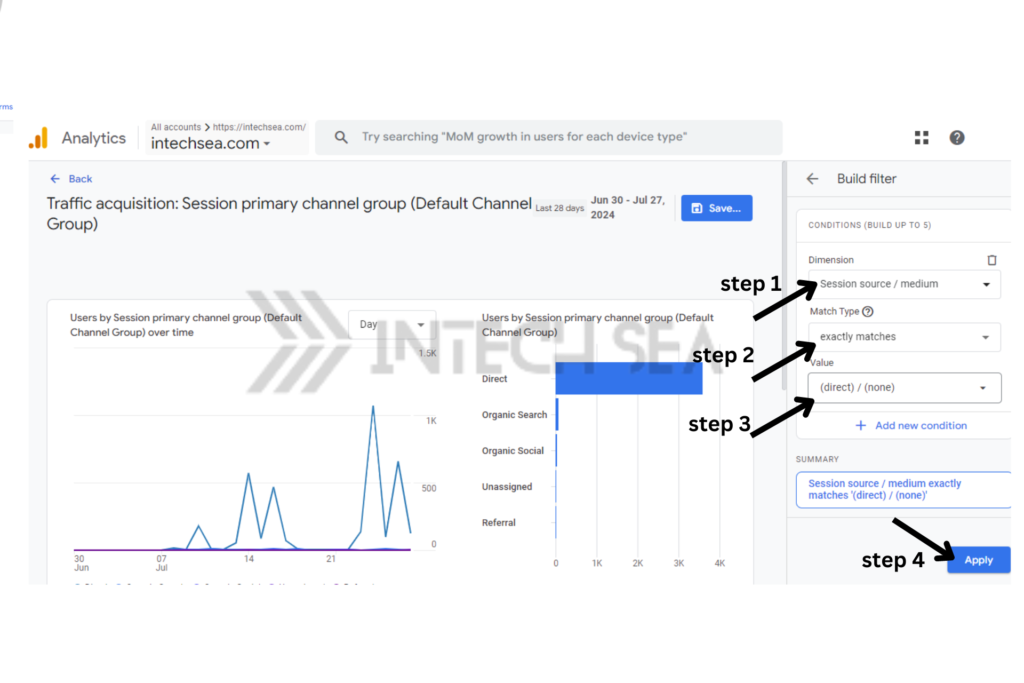
- Use the Comparison Feature • Click the “Comparison” button at the top of the report. • Select “Session source/mmedium” as the dimension. • This helps identify if certain sources are being misattributed as direct
- Examine User Behavior • Go to “Reports” > “Engagement” > “Pages and screens” • Add “Session source/mmedium” as a secondary dimension • Filter for “(direct) / (none)” to see how direct traffic users interact with your site.
- Check for self-references. • In the traffic acquisition report, look for your own domain in the referral sources. • If present, this indicates a tracking issue that may inflate direct traffic
- Investigate Dark Social Traffic • Look for landing pages that are typically shared on social media or messaging apps • High direct traffic to these pages may indicate dark social traffic
- Use UTM Parameters for Campaign Traffic • For any campaigns you’re running, ensure you’re using UTM parameters • Check if traffic from these campaigns is showing up correctly and not as direct.
- Set Up Custom Channel Groupings • Go to “Admin” > “Channel settings” > “Channel grouping” • Create rules to properly categorize traffic that might be misattributed as direct
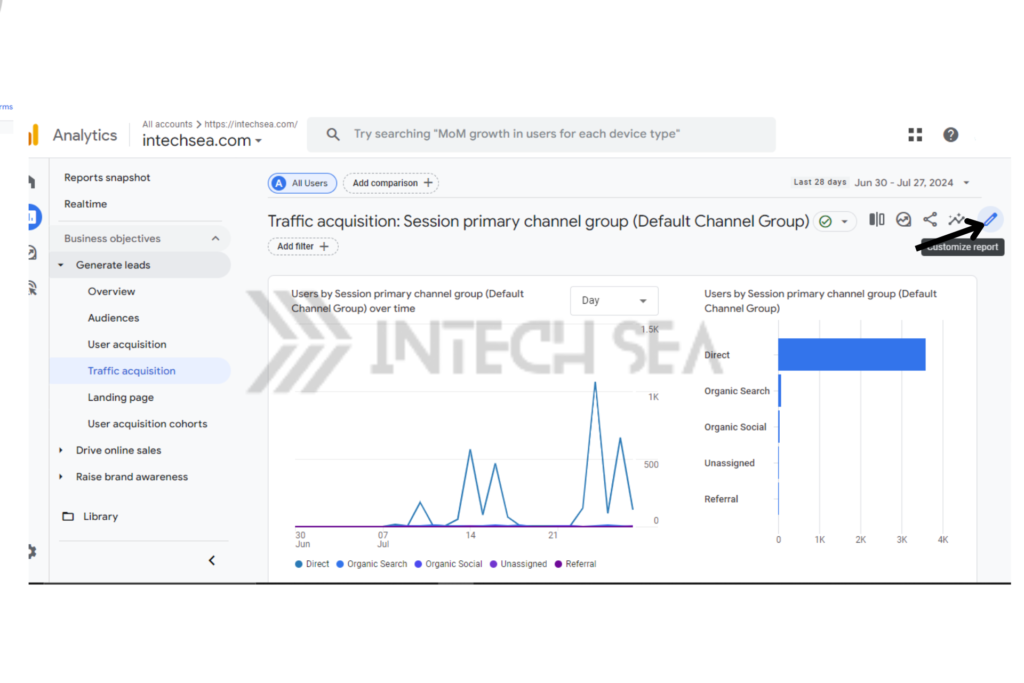
- Analyze direct traffic over time. • In the traffic acquisition report, adjust the date range. • Look for spikes in direct traffic that might correlate with specific events or campaigns.
- Use Google Analytics Debugging Tools • Install the Google Analytics Debugger Chrome extension; • Visit your site and check if all pages are sending data correctly to GA4.
- Cross-Reference with Server Logs • If you have access, compare GA4 data with your server logs • This can help identify traffic sources that GA4 might be missing.
- Set Up Custom Dimensions • Go to “Admin” > “Custom definitions” > “Create custom dimensions.” • Create dimensions to capture additional data that might help identify traffic sources.
- Use the Google Analytics Measurement Protocol. • For any custom applications or offline interactions, use the Measurement Protocol to send data to GA4. This ensures these interactions are properly attributed and not counted as direct traffic.
- Regularly audit your tracking setup. • Use tools like GACP (Google Analytics Checker Pro) to verify your tracking implementation. • Check for missing tags, incorrect implementations, or other issues that could lead to misattribution.
By following these steps, you can gain a more accurate understanding of your direct traffic sources in GA4. Remember, this process often requires ongoing monitoring and adjustment as your site and traffic patterns change over time.
Table Of Content
Introduction
Understanding the source of direct traffic in Google Analytics GA4 data is critical for analyzing accurate information and developing an effective marketing strategy. Direct traffic in GA4 refers to those visits where the source remains unknown or untracked and could possibly lead to mis-attributing data, thus clouding the view of user behavior and marketing performance.
A Groupon study has indicated up to 60% of traffic labeled “direct” in Google Analytics may come from some other source. This underscores the importance of accurately identifying and categorizing direct traffic to allow for precise analytics reporting and help inform irstb decisions.
What is Direct Traffic in GA4?
Direct traffic in GA4 refers to website visits where the traffic source cannot be determined. This occurs in several scenarios:
- Users manually enter the URL in their browser.
- Clicks from bookmarked pages
- Some email clients or messaging apps remove referral data.
- Issues with tracking code implementation
According to a BrightEdge study, organic search generates 53% of traffic on websites, whereas direct traffic accounts for about 15%. Nevertheless, direct traffic percent points are inflated due to misattribution. This reflects the importance of properly tracking and analyzing it.
The impact of misattributed direct traffic on data accuracy can be significant. It can lead to undervaluing certain marketing channels and overestimating brand strength. By properly identifying the true sources of direct traffic, businesses can allocate resources more effectively and optimize their marketing efforts.

Causes of Direct Traffic in GA4
Manual URL Entry and Bookmarks
When users type a website address directly or use a bookmark, GA4 typically records this as direct traffic. This often indicates strong brand awareness or successful offline marketing efforts. Research by Nielsen shows that 66% of brand searches are driven by offline media, potentially leading to direct URL entry.
While this type of direct traffic is genuine, it’s important to distinguish it from other sources to accurately gauge brand strength and the effectiveness of offline marketing initiatives.

Missing or Broken Tracking Code
If GA4 tracking code is missing from certain pages or not functioning correctly, visits to those pages may be logged as direct traffic. A study by Littledata found that 12% of e-commerce sites have broken or are missing Google Analytics tracking.
Regular audits of tracking code implementation across all pages can help identify and fix these issues, ensuring more accurate traffic attribution.
Ad Impressions and Dark Social
Some traffic from social media or messaging apps may appear as direct due to stripped referral data. This “dark social” traffic can account for up to 84% of outbound sharing, as reported by RadiumOne.
Understanding the impact of dark social on direct traffic is crucial for accurately assessing the effectiveness of social media marketing efforts and word-of-mouth referrals.
How to View Direct Traffic in GA4
To access and analyze direct traffic data in GA4:
- To identify direct traffic sources in GA4:
- Open GA4
- Go to Acquisition > Traffic Acquisition
- Find “Direct” in the report.
- Add “Landing page” as a secondary dimension.
- Look for patterns in landing pages.
- Use UTM parameters for campaigns.
- Check for self referrals.
- Monitor dark social traffic.
Adding dimensions like landing page or user type provides more detailed information. Google reports that adding just one additional dimension to reports can increase insight discovery by 42%.
The Traffic Acquisition Report in GA4 provides insight on how users are discovering your website. It helps you compare direct traffic to other channels to determine how effective your marketing strategies are in relation to each other and where improvements can be made.
How to Categorize Direct Traffic
Implementing UTM parameters
UTM parameters are tags added to URLs to track specific campaigns or sources. They play a crucial role in accurate traffic attribution. A Campaign Monitor survey found that 67% of marketers use UTM parameters to track their campaigns.
UTM parameters allow for precise tracking of marketing campaigns across various channels. By consistently using UTM tags, you can significantly reduce the amount of misattributed direct traffic and gain clearer insights into the performance of your marketing initiatives.
Using Advanced Tools
Tools like Semrush can offer deeper insights into traffic sources. Integrating these with GA4 helps uncover hidden patterns in your traffic data. Marketers using advanced analytics tools report 1.6 times more ROI improvement, according to a Google and Econsultancy study.
These tools can help identify potential sources of direct traffic by analyzing factors such as user behavior, landing pages, and engagement metrics. This additional context can be invaluable in understanding the true origins of your website traffic.

How to Reduce Direct Traffic in GA4
In Google Analytics, you can decrease direct traffic in the following ways:
- Put UTM parameters into practice.
- Establish tracking for first-party attribution.
- For ad views, use impression attribution.
- Switch to HTTPs
- Steer clear of vanity URLs.
- Verify the GA4 code you have.
- Stop internal communication.
- It can be WordPress plugin like: Airlift (It can can crawled your website pages and every it will it will count as Direct traffic ) (It happend to me)
Ensure Proper GA4 Setup
Regular checks of GA4 implementation help catch tracking issues:
- Verify the tracking code on all pages.
- Check for correct event tracking.
- Ensure cross-domain tracking is set up properly.
A Databox study found that 68% of marketers check their analytics at least once a week, helping to quickly identify and fix issues. This regular monitoring is essential for maintaining data accuracy and ensuring that all traffic sources are properly attributed.
Fixing Redirects and Link Shorteners
Properly set up redirects and link shorteners to maintain referral data. This is particularly important when moving from HTTP to HTTPS. BuiltWith reports that 95% of the top 1 million websites now use HTTPS, making this a common transition point.
When implementing redirects or using link shorteners, it’s crucial to ensure that referral information is passed correctly. This helps prevent unnecessary inflation of direct traffic numbers and provides a more accurate picture of your traffic sources.
Monitoring and improving direct traffic tracking
Regular Audits
Conduct frequent audits of your website and analytics setup. Tools like Screaming Frog can check for broken links or missing tags. An Ahrefs survey found that 66.5% of SEO professionals perform technical SEO audits monthly or more frequently.
These audits should include:
- Checking for consistency in tracking code implementation
- Verifying that all pages are properly tagged
- Ensuring that internal links are correctly set up to pass referral data
Educating Teams
Ensure all team members understand the importance of proper tracking and UTM usage. This significantly improves data accuracy. A Forrester study shows that companies adopting data-driven marketing are six times more likely to be profitable year-over-year.
Provide training on:
- The importance of consistent UTM tagging
- Best practices for implementing tracking codes
- How to use GA4 reports to gain insights
By fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making, you can improve the overall quality of your analytics data and make more informed marketing decisions.
Advanced Techniques for Direct Traffic Analysis
Custom Reports and Segments
Utilize GA4’s custom reporting features to gain deeper insights into your direct traffic. Create segments based on factors such as landing pages, user behavior, or conversion paths. This can help identify patterns in your direct traffic that may point to specific sources.
Cross-Domain Tracking
If your business operates across multiple domains, proper cross-domain tracking is essential to prevent inter-domain traffic from being misattributed as direct. Ensure that your GA4 setup correctly tracks user journeys across all your domains for a complete picture of user behavior.
Integrating with Google Search Console
Combine data from GA4 with Google Search Console to identify potential organic search traffic that may be misattributed as direct. This integration can provide valuable insights into keyword performance and help refine your SEO strategy.
Conclusion
The understanding and management of direct traffic in GA4 are quite critical for valid data analysis and marketing decisions. Through proper tracking, usage of UTM parameters, and periodic auditing of your setup, you can find it easier to understand where your visitors are coming from.
Apart from that, analysis for improvement is not done once. Due diligence in monitoring, a steady implementation of best practice across the board, and constant education of people involved in the process help in ensuring data integrity and better marketing.
By taking a proactive approach to managing direct traffic in GA4, you can:
- Improve the accuracy of your marketing attribution.
- Gain deeper insights into user behavior.
- Optimize your marketing spend more effectively.
- Make data-driven decisions with greater confidence.
As digital marketing continues to evolve, it is increasingly relevant to remain on top of your analytics data. Mastering how direct traffic in GA4 is identified and understood will put you in a great position to address changes in the digital landscape and push your marketing further.
FAQs
What is an example of direct traffic?
Direct traffic could be a user typing in your web address directly in their search bar or it being autofilled. There are a number of reasons why you could be seeing high levels of direct traffic. Understanding why and troubleshooting them is key.
What causes direct traffic spikes in Google Analytics?
Spikes in direct traffic could be a result of a successful brand awareness campaign. It could be caused by a number of things, which is why it’s so important to properly track your traffic and your leads to understand the impact of your marketing.
How can you reattribute direct traffic in Google Analytics?
You can’t move traffic around once it’s been logged. But you can put steps in place to fix high levels of inaccurate direct traffic. This includes using an attribution tool, using tagged URLs, and checking your codes are firing correctly.
How do I identify the source of direct traffic in GA4?
Using the traffic acquisition report in GA4, you can apply filters and dimensions to analyze where direct traffic is coming from. Implementing UTM parameters and using custom reports also help in identifying sources.
How to reduce direct traffic in GA4?
To reduce direct traffic, ensure proper GA4 setup, implement consistent UTM tagging, fix misconfigured redirects, and regularly audit your tracking setup for missing tags or broken links.
Is direct traffic always bad?
Not necessarily. Direct traffic can indicate strong brand awareness and user loyalty. However, unusually high direct traffic may point to tracking issues that need to be addressed.







