When used in SEO, GEO means the planning of content and keywords to suit some particular area. With the advent of AI-based search engines, GEO has become synonymous with Generative Engine Optimization, which concerns itself with bettering the content for the AI-search engines results.

What Does GEO Refer In The Field Of SEO?
Search engine optimization (SEO) historically associatively referred to geographic optimization: tailoring content and keywording to specific locations. This meaning, however, expands as AI-driven search engines grow in prevalence to encompass Generative Engine Optimization-the creation of entirety of content before a search engine itself that is meant to be generated solely from AI-generated material.

What is GEO (Geographical Optimization)
Geographical Optimization is the very process of customizing online content, keywords, and marketing strategies for target geographic locations. It is an extremely important strategy for businesses and services that depend on attracting a local clientele or audience. By obtaining visible listing of the business within local search results, it is easy for potential customers to find the business and contact them fast through someone close to them.
Key Aspects of Geographical Optimization:
- Local Keywords:
- Incorporating location-specific keywords into website content, meta tags, and descriptions to improve search engine rankings for local queries.
- Incorporating location-specific keywords into website content, meta tags, and descriptions to improve search engine rankings for local queries.
- Google My Business (GMB) Optimization:
- Setting up and managing a Google My Business, comprising detailed business information, pictures, reviews, and frequent updates to enhance visibility on local searches.
- Setting up and managing a Google My Business, comprising detailed business information, pictures, reviews, and frequent updates to enhance visibility on local searches.
- Local Backlinks:
- Building backlinks from local websites, directories, and community resources to boost local SEO authority.
- Building backlinks from local websites, directories, and community resources to boost local SEO authority.
- NAP Consistency (Name, Address, Phone Number):
- The business name, address, and phone number must be kept consistent across all online platforms and directories so that a search engine’ trust and local search become highly honored.
- The business name, address, and phone number must be kept consistent across all online platforms and directories so that a search engine’ trust and local search become highly honored.
- Local Content:
- Creation of relevant local content, which includes local events, news, or community activities on websites or blogs.
- Creation of relevant local content, which includes local events, news, or community activities on websites or blogs.
- Online Reviews and Reputation Management:
- Encouraging and developing online reviews on Google, Yelp, and other local review sites in order to instill trust and boost rankings in local searches.
- Encouraging and developing online reviews on Google, Yelp, and other local review sites in order to instill trust and boost rankings in local searches.
- Localized Landing Pages:
- Creating dedicated landing pages for different locations or service areas, each optimized with local keywords and information.
- Creating dedicated landing pages for different locations or service areas, each optimized with local keywords and information.
- Schema Markup:
- Using schema markup for local businesses to provide detailed information about the business to search engines, thus helping the business appear in local search results.
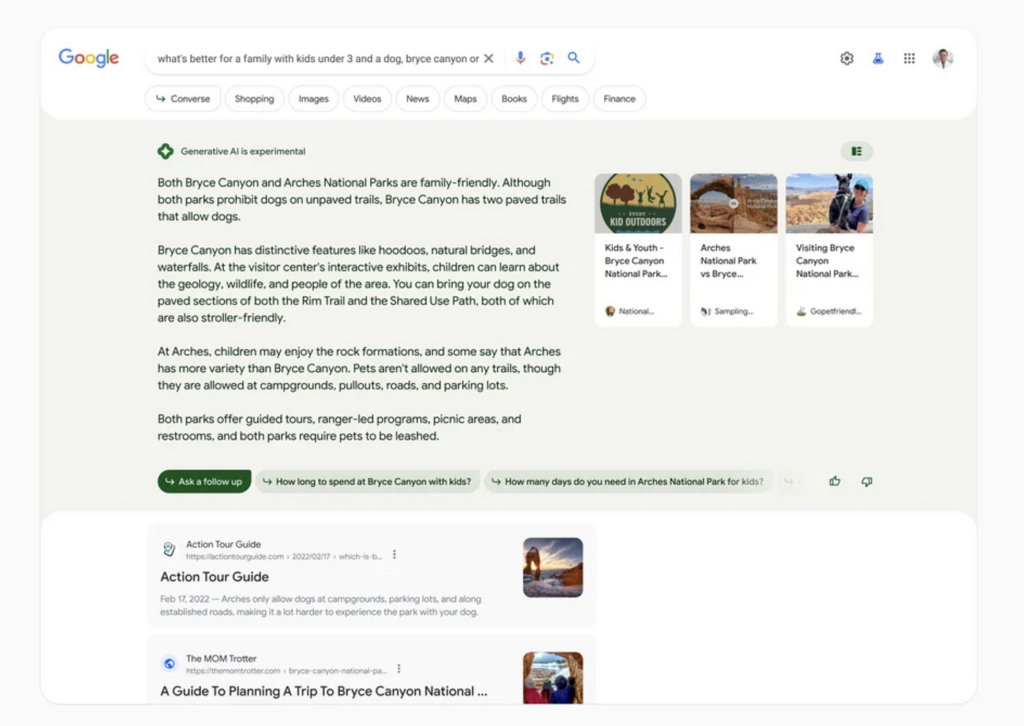
What is GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)
As of my last update, “Generative Engine Optimization” (GEO) is not a widely recognized term in the field of SEO. However, if it has emerged since then, it seems to denote a concept where optimization efforts are directed towards aligning content with the algorithms and criteria used by AI systems to generate search responses. In this context, “Generative Engine” may refer to the AI algorithms that power search engines.
If GEO has evolved into a recognized concept, it likely involves strategies focused on understanding and optimizing content to meet the preferences and requirements of AI-driven search engines. This could include considerations such as natural language processing, user intent analysis, and semantic search. In essence, GEO in this context would aim to improve a website’s visibility and ranking in search engine results by catering to the mechanisms through which AI systems generate search responses.
Which one is better GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) or Geographical Optimization
The choice between GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) and Geographical Optimization will depend on the specific goals, target audience, and the nature of the business. A comparative analysis on selecting the best option based on different scenarios is provided here.
The Difference Between GEO (Generative Engine Optimization), SEO and Geographical Optimization
Certainly! Here’s a comparative chart that highlights the differences between GEO (Generative Engine Optimization), SEO (Search Engine Optimization), and Geographical Optimization:
| Feature/Aspect | GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) | Geographical Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Optimization for generative AI engines to enhance content creation. | Tailoring content and strategy for specific geographic locations. |
| Purpose | Improve AI-generated content quality and relevance. | Target and attract local audiences and customers. |
| Techniques | – Training data refinement<br>- Prompt engineering<br>- Model fine-tuning<br>- Ensuring AI content alignment | – Local keywords<br>- Google My Business optimization<br>- Local backlinks<br>- NAP consistency (Name, Address, Phone) |
| Key Metrics | – Content relevance<br>- User engagement<br>- AI output quality | – Local search rankings<br>- Map pack visibility<br>- Local traffic and leads |
| Tools Used | – AI training platforms<br>- Prompt design tools | – Local SEO tools<br>- Google My Business<br>- Citation management tools |
| Target Audience | Businesses and individuals using generative AI for content creation. | Local companies and services that want to draw in clients from the area. |
| Content Focus | AI-generated content across various formats (text, images, etc.). | Localized content, local landing pages, and geo-specific information. |
| Examples of Application | Optimizing chatbots, automated content generation, and personalized marketing messages. | Optimizing business listings, local directory entries, and region-specific promotions. |
| Challenges | – Ensuring AI produces accurate and brand-consistent content<br>- Keeping up with AI advancements | – Managing multiple locations<br>- Local competition<br>- Consistency of NAP across platforms |
| Evolution | changing quickly in tandem with machine learning and AI developments. | Growing importance with the rise of mobile searches and local intent. |
This chart provides a clear comparison of the three optimization strategies, highlighting their unique aspects and applications.
Summary
GEO refers to tailoring online content, keywords, and marketing strategies to target specific geographic locations. Key aspects of GEO include incorporating location-specific keywords into website content, meta tags, and descriptions. GEO aligns content with the algorithms and criteria used by AI systems to generate search responses. The choice between GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) and Geographical Optimization depends on the specific goals, target audience, and nature of the business.







